In this tutorial we will discuss git bisect to find the commit that caused regression bug.
Regression Bug
A regression bug is an error that appears in software after a change like a new feature, update, or fix causing previously working functionality to break.It indicates the system has “regressed” in quality. This can happen in typical software development.
What is Git Bisect?
Let’s understand the problem :
We know a feature was working before, now it’s broken. How do we find which commit broke it – without checking every commit?
The Solution is git bisect!
Git Bisect helps find the exact commit that introduced a bug using binary search.
The Core Idea Behind Git Bisect
Binary Search is a fast way to find something inside a sorted list. Instead of checking items one by one, it splits the list in half each time reducing search time from O(n) to O(log n).
Let’s see an example searching for 7 in a sorted list as shown below.
List: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
Search for “7”
↓
Step 1 → middle = 4 (not found)
Search right half → [5,6,7,8]
Step 2 → middle = 6 (not found)
Search right half → [7,8]
Step 3 → middle = 7 (FOUND)Instead of checking 8 items, it found the answer in just 3 checks.
The same technique is used in git bisect to search for the commit that caused the bug.
How to use git bisect
Suppose we have simple calculator app with following commits. (We introduced a bug in commit 57cd4b8 for this demo)
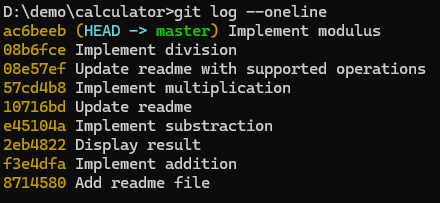
The latest code is shown below commit ID : ac6beeb
def add(a :int, b :int) -> int:
return a - b
def subtract(a :int, b :int) -> int:
return a - b
def multiply(a :int, b :int) -> int:
return a * b
def divide(a :int, b :int) -> float:
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("Cannot divide by zero.")
return a / b
def modulus(a :int, b :int) -> int:
return a % b
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = add(3, 5)
print(f"The sum of 3 and 5 is: {result}")
We can see that add function is wrong when we run the application we will get the below output
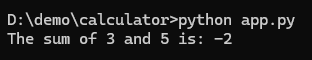
Now we have a regression bug, we need to find out the which commit introduced this bug. To finding this bug manually we need to test each commit for the bug, but git bisect will help us to find the buggy commit faster.
First run the below command to list all the commits with commit IDs.
git log --onelineRun the below command to start the git bisect process :
git bisect start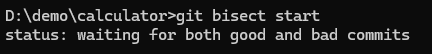
Next we need to give one known good commit where the feature(additon) worked and bad commit. We are going to use use the first commit for this demo (You can give previous good release commit ID)
git bisect good 8714580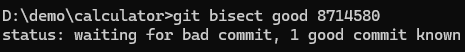
Finally, we need to give a bad commit for this demo Im using latest commit ID ac6beeb :
git bisect bad ac6beeb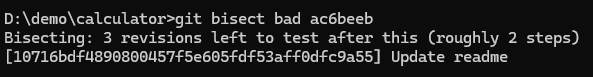
From the above logs we can see that bisecting started current commit is “update readme”. Let’s check app output
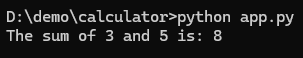
It is working fine – the answser is correct, next we need to mark it as good by running the below command
git bisect good
We are now moved to another commit that is “Update readme with supported operations”, again run the application or run unit tests.
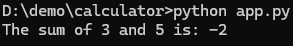
Yes we got bad commit, mark it using the below command.
git bisect bad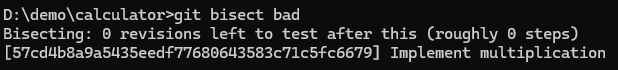
We finally found the commit that caused the bug that is “Implement multiplication”, commit ID : 57cd4b8.
Finally , we need to exit git from bisect mode by running the below command
git bisect reset
Conclusion
With Git Bisect, you let Git do the detective work for you – using the power of binary search to find the exact commit that introduced a bug. It’s fast, reliable, and perfect for regression issues. I hope this tutorial helpful for you. Learn the difference between git rebase and git merge.
